COMPOSITE IMAGE: DANIELLA MARIE AGACER FROM REUTERS, AFP, STOCK PHOTOS
MANILA, Philippines—Southeast Asia, together with the Philippines, faces quite a lot of challenges, like poverty and lack of entry to high quality schooling, which the United Nations Kids’s Fund (Unicef) mentioned are inextricably linked to youngsters’s studying outcomes.
In response to evaluation of outcomes of the Southeast Asia Main Studying Metrics (SEA-PLM) 2019, which was launched this yr, most Filipino Grade 5 college students wouldn’t have the minimal studying and mathematical abilities anticipated on the finish of major schooling.
Unicef had harassed that due to this, there may be a direct have to harness the potential of early childhood schooling because it was anticipated to supply a “very important basis for lifelong studying.”
Nevertheless, in its second evaluation of the findings of the most recent SEA-PLM, Unicef said that there’s a “essential hyperlink between youngsters’s studying outcomes and their general wellbeing,” too.
In response to Unicef, the secondary analysis confirmed that “youngsters who carry out nicely academically are inclined to have higher social and emotional wellbeing, in addition to higher bodily well being.”
Conversely, “those that wrestle with their research are at a better threat of experiencing psychological well being issues and poorer well being outcomes,” Unicef mentioned because it launched its newest report “What Does SEA-PLM 2019 Inform Us About Youngster Properly-Being and Studying in Six Southeast Asian Nations?”
The report delved into the connection between Grade 5 college students’ wellbeing and studying in six nations within the area, together with the Philippines, and recognized key components that contributed to raised outcomes in these studying areas:
- Studying
- Writing
- Arithmetic
Lack of studying, math abilities
By means of the Sustainable Growth Objectives (SDGs), the UN in 2016 known as for entry to high quality fundamental schooling for all youngsters, together with some 30 million learners within the Philippines.
Because the UN harassed, this was to steer college students to related studying outcomes and equip them with required abilities, particularly in language and arithmetic, as early as kindergarten.
GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
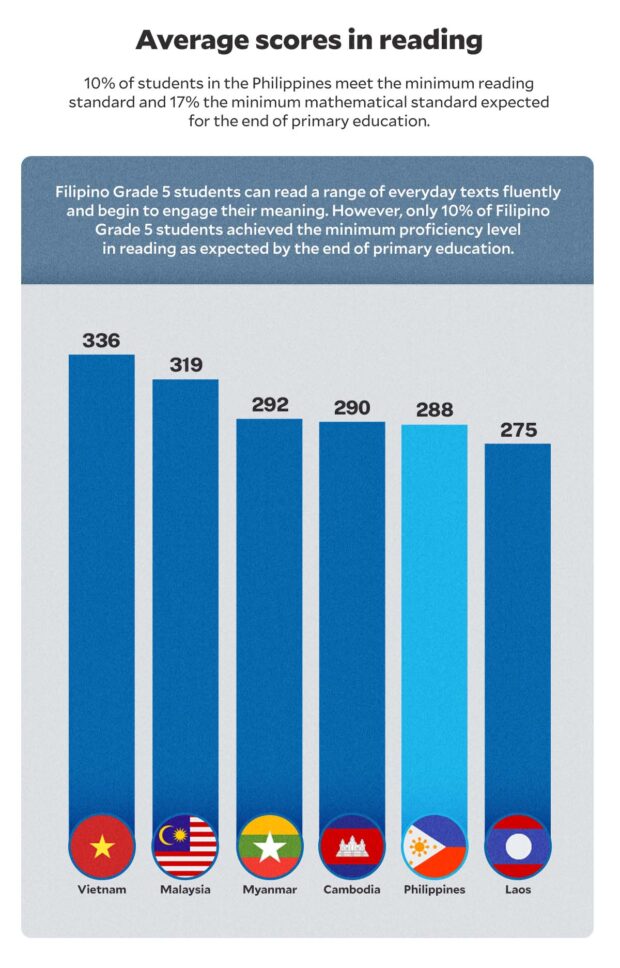
This, as solely 10 % of scholars within the Philippines met the minimal studying normal and 17 % met the minimal mathematical normal anticipated on the finish of major schooling, as supplied in SDG 4.1.1—Schooling Proficiency.
Filipino Grade 5 college students acquired a median rating of 288 in studying evaluation, which signifies that they will learn a spread of on a regular basis texts fluently and comprehend their that means.
The issue, nevertheless, is that solely 10 % achieved the minimal proficiency degree, which is the flexibility to grasp texts with acquainted constructions and handle competing data.
GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
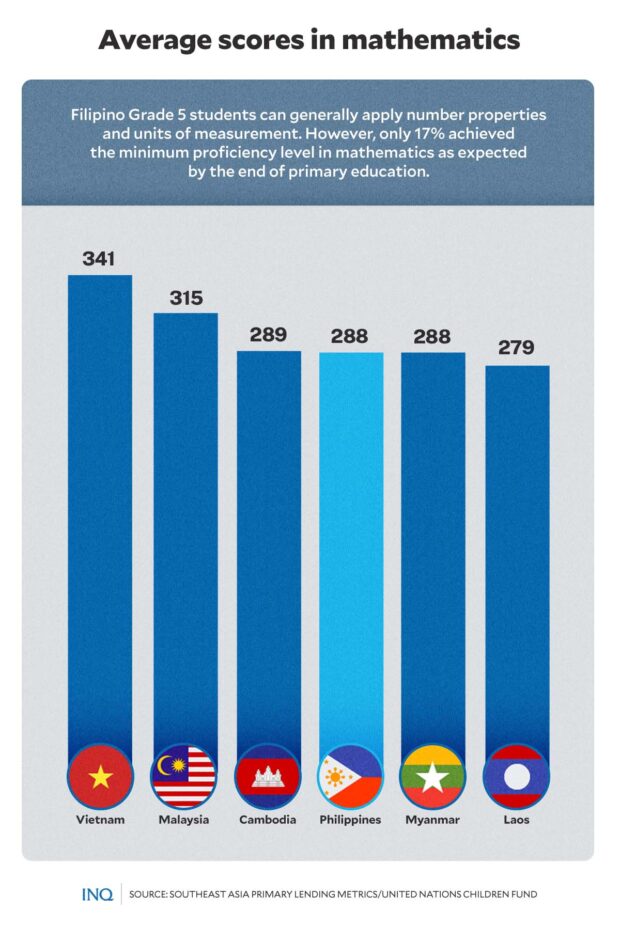
With regards to arithmetic evaluation, Filipino Grade 5 college students additionally acquired a rating of 288, indicating that they will usually apply quantity properties and items of measurement.
However, just like the consequence within the studying evaluation, Unicef mentioned solely 17 % had the flexibility to carry out mathematical operations, together with fractions and interpret tables and graphs.
GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
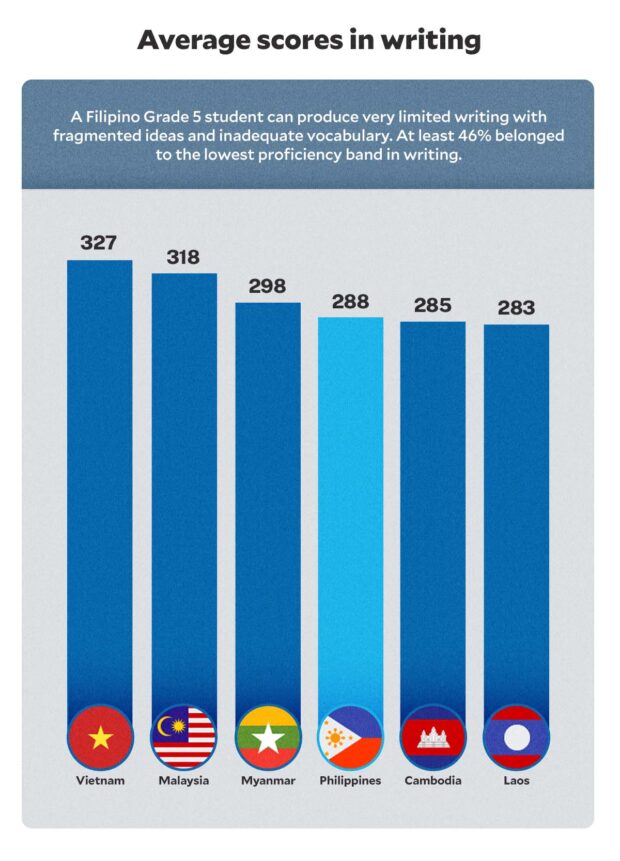
As to writing evaluation, Filipino Grade 5 college students additionally acquired a rating of 288, suggesting {that a} pupil can produce very restricted writing with fragmented concepts and insufficient vocabulary as some 46 % fell to the bottom proficiency band in writing.
Wellbeing and higher studying
Unicef mentioned “the hyperlink between a toddler’s wellbeing and studying outcomes is mutually reinforcing and interconnected” as research have proven that youngsters with increased ranges of wellbeing have increased ranges of educational engagement and achievement.
“These wellbeing domains are critically essential through the impressionable stage of early adolescence, when quickly occurring bodily, emotional and social adjustments have an effect on youngsters’s well-being and studying,” it mentioned.
As defined by Unicef, its secondary analysis, which was derived from the findings of the SEA-PLM 2019, took a better have a look at the connection between studying and wellbeing throughout these key components:
- Psychological wellbeing, which included family setting (parental engagement, parental expectations, studying sources), social setting at college (peer relationships, attitudes in direction of faculty, youngsters’s voices) and publicity to violence at college
- Bodily wellbeing, which included youngsters’s time use and actions (out-of-school actions, time to get to highschool, amenities at college, amenities in the local people), and well being and diet (meals on a traditional day, entry to WASH at college)
- Social and environmental context, which included worries in regards to the setting (environmental issues) and studying in regards to the setting (realized some/so much at college about environmental points, taking motion, duty)
The evaluation thought of that “a toddler’s wellbeing is influenced by goal and subjective components together with: their very own actions, experiences and relationships; the networks and sources of their caregivers; and public insurance policies and nationwide context.”
Parental engagement, entry to books
The primary issue, which is a conducive dwelling setting with extra parental engagement and entry to books, resulted in higher studying outcomes in Southeast Asia, primarily based on findings from these six collaborating nations:
- Cambodia
- Lao PDR
- Malaysia
- Myanmar
- Philippines
- Vietnam
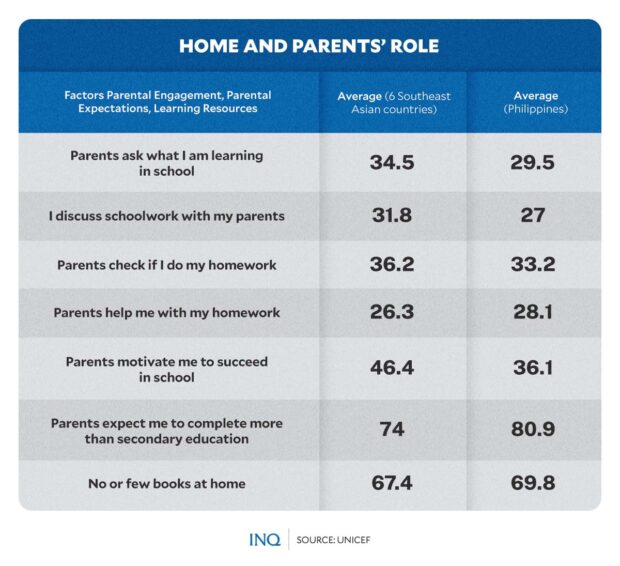
Nevertheless, Unicef mentioned throughout the six collaborating nations, the Philippines “notably confirmed the very best hole in outcomes between youngsters of extremely engaged mother and father and youngsters of low-engaged mother and father.”
GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
Based mostly on SEA-PLM 2019 knowledge, the share of youngsters with mother and father who ask what their youngsters study in class was 29.5 %, decrease than the 34.5 % regional common.
Unicef mentioned parental engagement in youngsters’s studying differed by nation, with youngsters in Vietnam having the very best percentages in virtually all types of engagement in contrast with the remainder of the nations included within the report.
On entry to books, 69.8 % of Grade 5 college students within the Philippines had no or few books at dwelling, barely increased than the 67.4 % regional common however approach decrease than Cambodia’s 69.4 %, Malaysia’s 83.9 %, and Lao PDR’s 83 %.
Likewise, there have been extra college students within the Philippines who said that their mother and father count on them to finish greater than secondary schooling at 80.9 %, which is increased than the 74 % regional common.
However on the identical time, the Philippines had the least share of fogeys who inspire their youngsters to reach faculty as its 36.1 % was approach decrease than the 5 nations’ 58.5 %, 50.7 %, 48.6 %, 48 %, and 40.5 %.
As defined by Unicef, earlier literature prompt that these components are positively linked with studying as a result of “when college students are comfortable, their anxiousness decreases, well being is healthier, faculty attendance and efficiency enhance, and relationships are simpler.”
Protected colleges
A protected and supportive faculty setting performs a giant position in studying outcomes, too.
Unicef mentioned knowledge indicated {that a} sense of belonging, safety, and goal at college helped youngsters carry out higher. Conversely, decrease scores and high quality of life have been related to publicity to violence at college.
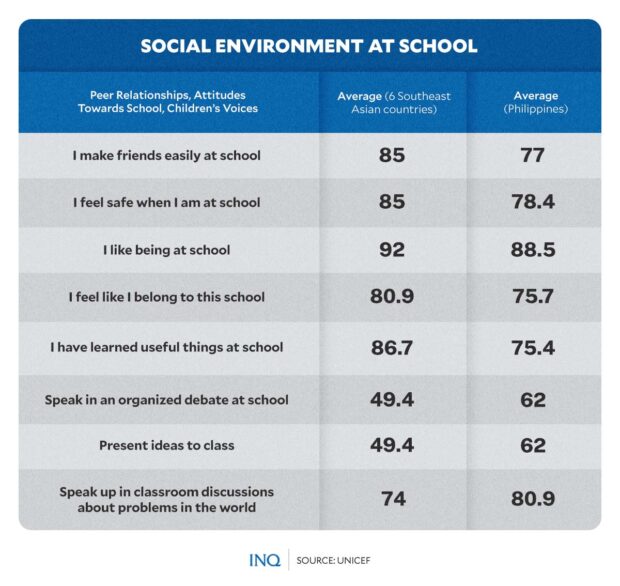
SEA-PLM 2019 knowledge confirmed that on common, virtually 9 out of 10 youngsters within the area discovered it straightforward to make associates at college, no matter gender or location.
GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
However youngsters within the Philippines had the bottom common, with solely 77 % of youngsters discovering it straightforward to make associates at college. Kids in Vietnam had the very best common at 94.4 %, even increased than the 85 % regional common.
“Kids’s social abilities and skill to make associates may positively have an effect on their educational accomplishments over time, as research point out that studying efficiency is said to see experiences,” Unicef mentioned.
On publicity to violence at college, the Philippines had the very best degree of bullying at 63 %, increased than Malaysia’s 25.9 %, Vietnam’s 18.4 %, Myanmar’s 13.2 %, Lao PDR’s 4 %, and Cambodia’s 2.4 %.

GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
The Philippines additionally had the very best ranges of vandalism, aggression, offensive habits, and violence, having a median of 39.4 %, 9.2 %, 28.8 %, and 12.3 %.
Kids’s actions
Kids’s actions–each out and in of college–are vital components that have an effect on studying.
Unicef, nevertheless, mentioned how a toddler spends time could rely on quite a lot of dimensions similar to parental involvement, socioeconomic circumstances, security and the supply of amenities in native communities.
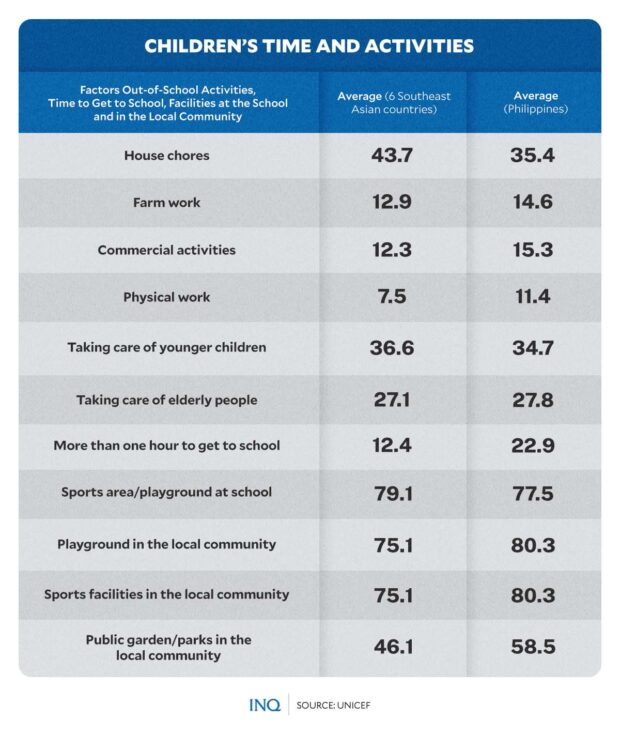
Based mostly on SEA-PLM 2019 knowledge, the Philippines had the very best degree of availability of playgrounds in native communities at 80.3 %, however the availability of such in colleges was the second lowest throughout the collaborating nations within the area.
GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
The Philippines additionally had the very best share of youngsters taking multiple hour to get to highschool at 22.9 %, increased than Lao PDR’s 13.7 %, Myanmar’s 11 %, Malaysia’s 7.7 %, Cambodia’s 5.2 %, and Vietnam’s 1.3 %.
Unicef mentioned “the time youngsters spend commuting may have an effect on their skill to study. Lengthy commutes can distract them from their studying duties and intrude with their focus in class, owing to fatigue.”
Notably, nevertheless, in comparison with the remainder of the collaborating nations, there have been fewer Filipino youngsters who have been engaged in out-of-school actions similar to home chores (35.4 %), farm work (14.6 %), and business actions (15.3 %).
Well being, entry to WASH
As defined by Unicef, apart from making youngsters’s speedy environments protected and safe, “well being and diet have been simply as essential in making certain the bodily well-being of youngsters.”
It mentioned “ample water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) amenities in colleges contributed to increased studying,” stressing that these companies are particularly essential within the restoration from the COVID-19 disaster.
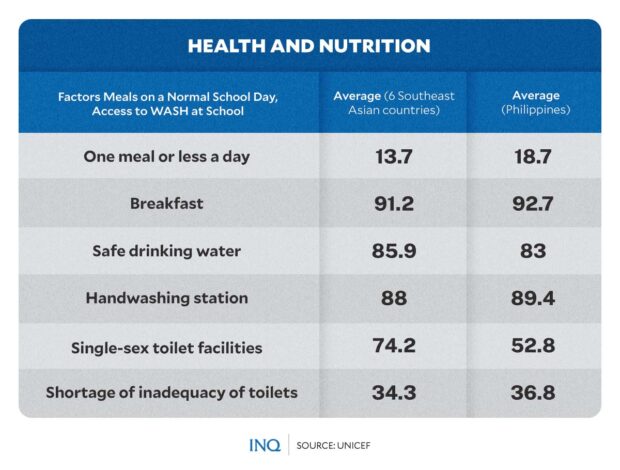
However Unicef mentioned as of college yr 2020-2021, the Division of Schooling discovered that 70 % of native public colleges nationwide nonetheless wouldn’t have the minimal amenities and provisions.
GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
Based mostly on SEA-PLM 2019 knowledge, entry to single-sex bogs was second lowest within the Philippines at solely 52.8 %, decrease than Cambodia’s 73.2 %, Vietnam’s 95.6 %, and Malaysia’s 96.2 %.
Likewise, the shortage of ample diet was linked to decrease scores.
Unicef mentioned 18.7 % of youngsters within the Philippines get just one meal and even much less a day, the very best in comparison with the remainder of the collaborating nations within the area.
A earlier report additionally discovered that regardless of extra youngsters surviving, tens of millions of Filipino youngsters are failing to develop nicely amid excessive ranges of stunting, losing, micronutrient deficiencies, and the fast-growing charges of being obese and weight problems.
A powerful constructive correlation was additionally present in a lot of the collaborating nations between youngsters’s concern for environmental sustainability points and their studying efficiency.

GRAPHIC Ed Lustan
“Research have proven that the local weather disaster disproportionately impacts youngsters who’re already falling behind of their schooling, particularly ladies,” Unicef mentioned.
It harassed that nations which can be at extraordinarily excessive threat to local weather change, just like the Philippines, even have the bottom ranges of major faculty completion and foundational studying abilities.
Gov’t wants to maneuver
Unicef mentioned governments throughout Southeast Asia “have a possibility to reshape their strategy to schooling in order that youngsters and adolescents are outfitted with the mandatory educational and socio-emotional abilities to dwell a rewarding life.”
“The latest COVID-19 pandemic created a possibility for governments and college techniques to rethink the way to strategy youngsters’s studying and to create insurance policies for extra resilient and inclusive societies,” mentioned Unicef.
Unicef mentioned it “recommends authorities establishments to work throughout sectors—colleges, mother and father, and communities—to help learners by way of direct engagement and fostering supportive environments.”
As harassed by Unicef Philippines Consultant Oyunsaikhan Dendevnorov, the report illustrated {that a} youngster’s wellbeing and studying outcomes are mutually reinforcing and interconnected.
“That is particularly essential for constructing foundational abilities and through early adolescence when speedy bodily, emotional, and social adjustments have an effect on development and growth,” he mentioned.
“The insights of youngsters on this report will assist authorities companions and colleges to mirror on the present insurance policies and practices and the way they are often improved,” he added.
TSB
Learn Subsequent
Subscribe to INQUIRER PLUS to get entry to The Philippine Every day Inquirer & different 70+ titles, share as much as 5 devices, take heed to the information, obtain as early as 4am & share articles on social media. Name 896 6000.
Credit score:Source link





